Struggling with stubborn facial pigmentation? This in-depth guide covers the causes, treatments, and best management strategies for melasma, sunspots, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, and more. Learn how to effectively fade dark spots using skincare, chemical peels, lasers, and essential sun protection. Discover expert insights on the latest treatments and why consistency is key to long-term results. Read on to regain clear, even-toned skin.
Understanding Causes, Treatments, and Management Approaches
Stubborn facial pigmentation is a common skin concern that can affect people of all ages, skin tones, and backgrounds. These dark patches or spots on the face can be frustrating and difficult to get rid of, often affecting self-confidence. Understanding what causes this pigmentation and the best ways to treat it can help manage the condition more effectively.
What Causes Facial Pigmentation?
Facial pigmentation happens when the skin produces too much melanin, the natural pigment that gives skin its colour. Common causes include:
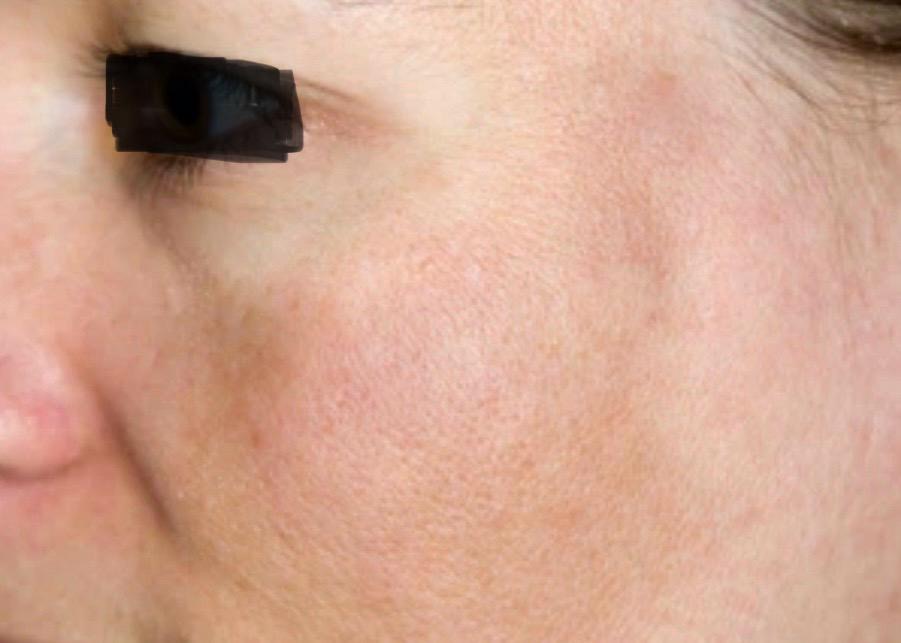
1. Melasma
Often triggered by hormonal changes during pregnancy, birth control use, or hormone therapy, causing brown patches on the forehead, cheeks, and upper lip.
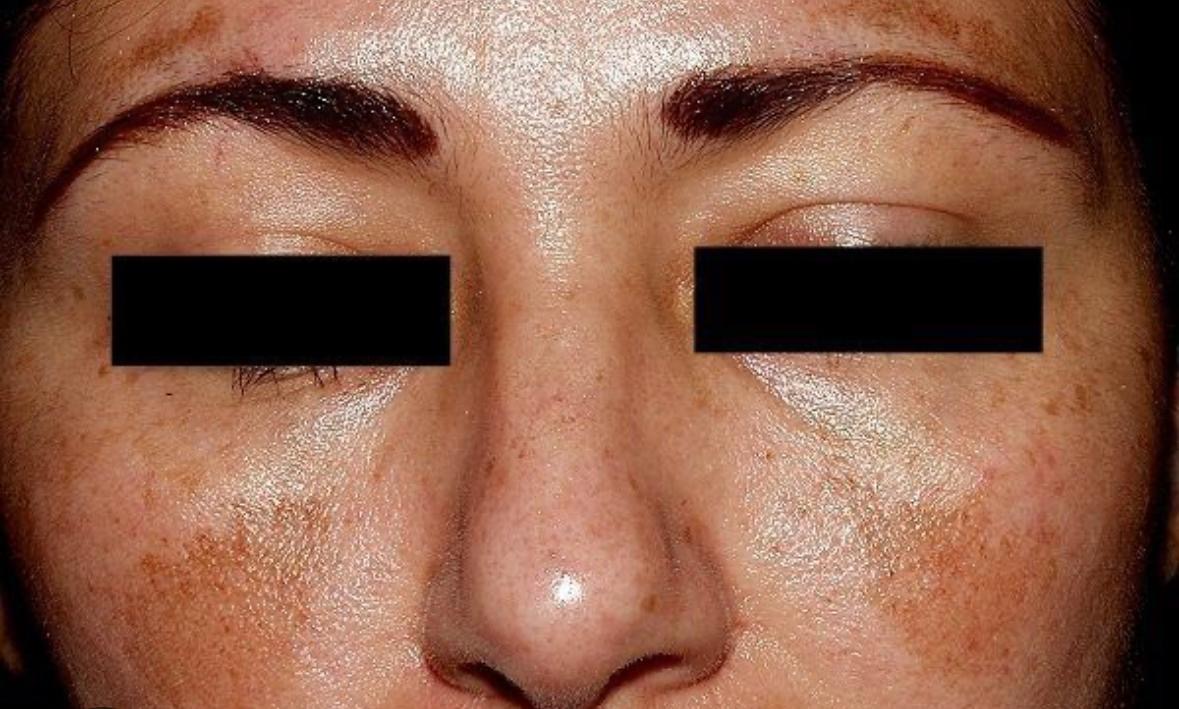
Figure 1. and Figure 2. Melasma
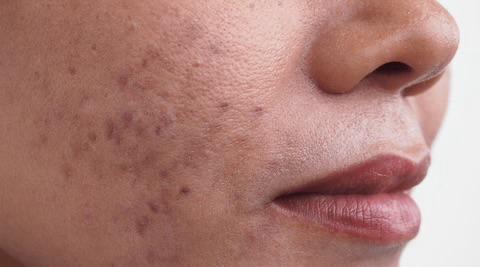
2. Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH)
Dark spots left behind after acne, eczema, or skin injury.
Figure 3. PIH
3. Sunspots (Solar Lentigines)
Small dark patches caused by sun exposure, commonly seen on areas exposed to the sun. These are also known as liver spots but is a misnomer and no indication of liver health.
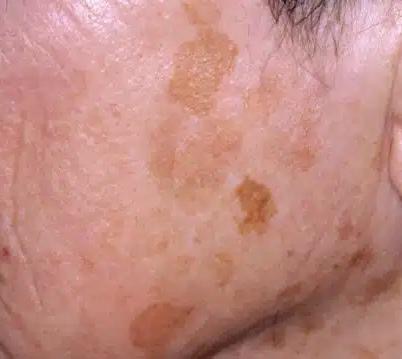
Figure 4. and Figure 5. Solar lentigos
4. Medication Side Effects
Some medications like certain antibiotics or pain relievers can cause skin discoloration.
5. Genetics
People with darker skin tones are more prone to pigmentation issues.
Clinical Presentation
Facial pigmentation usually appears as flat, dark spots or patches that can range from light brown to deep gray. The patches may be symmetrical, especially in melasma, and often show up on the cheeks, forehead, or upper lip.
How Is It Diagnosed?
Doctors typically diagnose facial pigmentation by looking at your skin and asking about your medical history. In some cases, special lights or magnifying tools can help determine how deep the pigmentation is. Rarely, a small skin sample (biopsy) may be taken to rule out other conditions.
Treatment Options
Getting rid of stubborn facial pigmentation can take time and often requires a combination of treatments. Here’s what works best:
1. Creams and Serums:
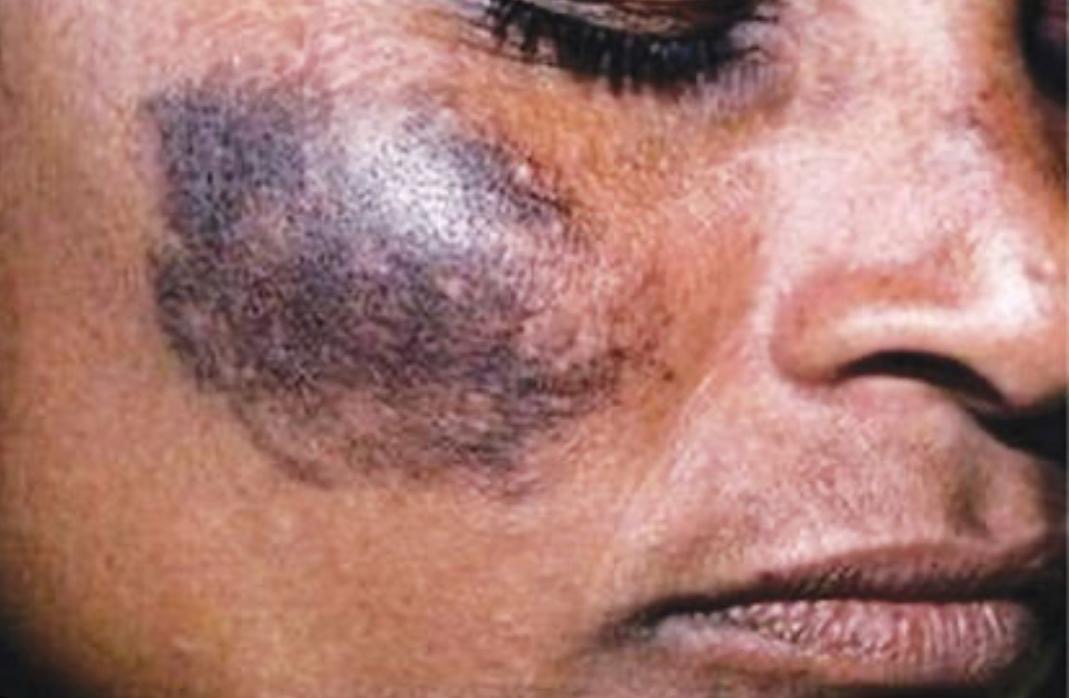
- Hydroquinone: A prescription topical agent renowned for its efficacy in lightening hyperpigmented lesions. However, its use demands meticulous caution and strict dermatological supervision. Misuse or prolonged, unsupervised application may paradoxically compromise the skin, resulting in exogenous ochronosis—a rare yet formidable disorder of pigmentation that is notoriously resistant to treatment. Though typically associated with the unregulated use of high concentrations found in illicit skin-bleaching products, ochronosis can also manifest with regulated formulations, hence the need for vigilant monitoring even with prescribed concentrations.
- Azelaic Acid: Helps fade dark spots and is also good for acne.
- Kojic Acid: A natural ingredient that reduces pigment production.
- Tranexamic Acid: Can be applied on the skin or taken as a tablet to treat melasma.
Figure 6. Cosmetic ochronosis
2. Chemical Peels:
- Treatments using glycolic acid or salicylic acid can remove the top layer of skin, revealing brighter skin underneath.
3. Laser and Light Therapy:
- Certain lasers and intense pulsed light (IPL) treatments can target pigmentation and break down melanin.
4. Oral Medications:
- Tranexamic Acid tablets have shown promise in treating melasma.
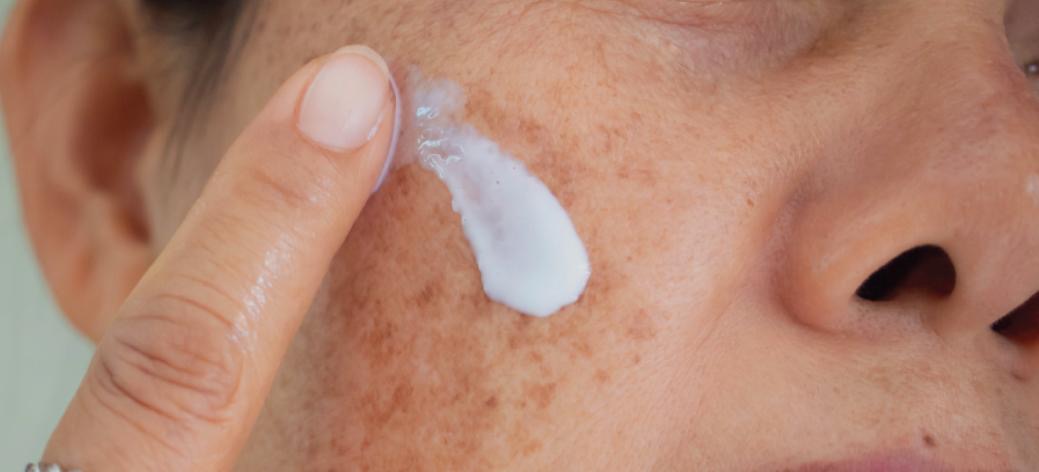
5. Sun Protection:
- Daily sunscreen use (SPF 30 or higher) once again, our best friend, sun block, is probably the best cream you can use to help prevent and improve pigmentation.
Figure 7. Sun block is essential for good outcomes
It is imperative to highlight that while the aforementioned treatment modalities can significantly improve pigmentation, and often involve significant cost, but their efficacy hinges on unwavering sun protection. A mere few minutes of unprotected sun exposure can swiftly undo the progress achieved, rendering the entire regimen futile. Before investing in pigmentation treatments, one must commit to rigorous, lifelong sun avoidance and diligent use of broad-spectrum sunscreens — without such dedication, the journey to clearer skin risks being in vain.
Why Is It Hard to Treat?
Facial pigmentation can be stubborn because it often has multiple causes and tends to come back, especially if the skin is exposed to sunlight. Treatments can take several months to show results, and consistency is key. Newer treatments like microneedling, platelet-rich plasma (PRP), and genetic-based therapies are being studied to improve outcomes.
In conclusion, stubborn facial pigmentation can be a long-lasting issue, but with the right combination of treatments and good sun protection, it can be managed effectively. Early treatment and patience are essential for the best results. Ongoing research into new therapies offers hope for more effective solutions in the future. So watch this space for updates!