Discover everything about sunscreen, from choosing between chemical and mineral options to understanding their benefits for different skin types. Learn how sunscreen works, tips for avoiding the white cast, and why broad-spectrum SPF 30+ is essential for protecting your skin. Get expert advice on application, safety, and environmental impact to ensure effective sun protection.
How do I choose my Sunscreen?
Sunscreen is a vital part of any skincare routine, helping to protect against the harmful effects of ultraviolet (UV) rays. However, choosing the right type can be confusing, especially when faced with options like chemical and mineral sunscreens. While both provide sun protection, they work in different ways and suit different skin types and preferences. This article explores the key differences between the two to help you make an informed choice.
Types of Sunscreen
1. Mineral
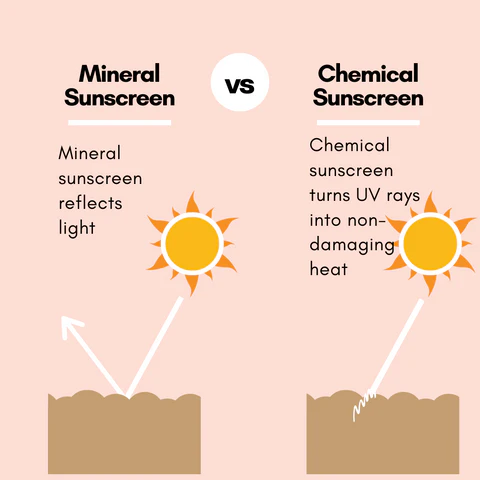
Mineral sunscreen works like a layer of tiny mirrors on your skin, bouncing the sun’s harmful rays away.
2. Chemical
An easy way to think of it is that chemical sunscreen acts like a sponge, soaking up the sun’s rays and neutralizing them to prevent any harm.
How They Work
-
Chemical Sunscreens
- Mechanism: Chemical sunscreens absorb UV rays and convert them into heat, which is then released from the skin. This is made possible by active ingredients such as avobenzone, oxybenzone, octisalate, and octocrylene.
- Application: These sunscreens need to be applied at least 15-30 minutes before sun exposure to ensure they are fully absorbed and effective.
-
Mineral Sunscreens
- Mechanism: Mineral sunscreens, often referred to as physical sunscreens, act as a barrier on the skin's surface. They reflect and scatter UV rays away from the skin. The active ingredients are typically zinc oxide and titanium dioxide.
- Application: These provide immediate protection upon application and do not require waiting time.
Key Differences
| Feature | Chemical Sunscreens | Mineral Sunscreens |
|---|---|---|
| Active Ingredients | Synthetic compounds like avobenzone, oxybenzone | Natural minerals like zinc oxide, titanium dioxide |
| How They Work | Absorb UV rays and convert them to heat | Reflect and scatter UV rays |
| Skin Sensitivity | May cause irritation or allergic reactions | Generally suitable for sensitive skin |
| Finish | Lightweight, blends easily, no white cast | May leave a white cast, thicker consistency |
| Protection | Effective against UVA and UVB, varies by formulation | Broad-spectrum by nature |
| Water Resistance | Often water-resistant formulations available | Many are water-resistant but may feel heavier |
| Reapplication | Requires reapplication after swimming or sweating | Same, though may wear off faster due to physical layer |

Advantages and Disadvantages
Chemical Sunscreens
- Pros:
- Lightweight and easy to apply.
- Works well under makeup.
- Does not leave a visible residue.
- Cons:
- Requires time to become effective after application.
- Can irritate sensitive skin or eyes.
- Some ingredients have raised environmental concerns, such as potential harm to coral reefs.
Mineral Sunscreens
- Pros:
- Gentle and suitable for sensitive or acne-prone skin.
- Provides immediate protection.
- Environmentally friendly options are available.
- Cons:
- May feel heavier on the skin.
- Can leave a white cast, particularly on darker skin tones.
Tips to minimize the white cast that mineral sunscreen can leave on darker skin tones:
- Rub First: Before applying, rub the sunscreen into your hands, then gently pat it onto your skin for a more even application.
- Try Tinted Options: Look for tinted mineral sunscreens that match your skin tone; they’re less likely to leave a visible cast.
- Transparent, Invisible, or Sheer Labels: Choose products labeled as “transparent,” “invisible,” or “sheer” to reduce the white residue.
- Prep with Moisturizer: Use a moisturizer before applying mineral sunscreen to make the cast less noticeable.
- Opt for Zinc Oxide: Zinc oxide-based sunscreens often create less of a white cast compared to titanium dioxide.
- Micronized Formulas: Brands with micronized particles often make the sunscreen appear invisible on the skin.
- Avoid Mixing Products: Don’t mix sunscreen with other products like moisturizer or foundation; this can dilute its effectiveness.
- Spray Sunscreen Safely: Apply in a well-ventilated area and avoid inhaling the product.
These adjustments can help make wearing mineral sunscreen a better experience while ensuring effective sun protection.
Who Should Use What?
-
Chemical Sunscreens are ideal for:
- People seeking a lightweight feel and invisible finish.
- Those who engage in sports or water activities, as water-resistant options are often more lightweight.
-
Mineral Sunscreens are best for:
- Individuals with sensitive, acne-prone, or reactive skin.
- Parents looking for safe options for children.
- Those who prefer natural or eco-friendly skincare products.
Although no SPF can block all UV rays, both mineral and chemical sunscreens have been shown to be effective in blocking the sun’s harmful UVA and UVB rays. According to the American Academy of Dermatology, regardless of whether you’re using chemical or mineral sunscreen, as long as you’re using one of them regularly and the SPF is 30 or higher, you’re being protected from 97 percent of the UV radiation.
Remember that sunlight can penetrate windows, allowing harmful UV rays to reach your skin. To protect against potential damage, it’s important to apply sunscreen even when staying indoors during daylight hours.

What is the best vehicle for sunscreen?
1. Creams and Lotions
- Best For: Normal to dry skin.
- Advantages:
- Hydrating, making them ideal for dry or sensitive skin.
- Easier to achieve even application.
- Use Case: Everyday use for both the face and body. Works well for children due to its moisturizing properties.
2. Gels
- Best For: Oily or acne-prone skin.
- Advantages:
- Lightweight and non-greasy.
- Absorbs quickly and doesn’t clog pores.
- Use Case: Great for humid climates or people with acne-prone skin.
3. Sprays
- Best For: Quick application and reapplication.
- Advantages:
- Convenient for large or hard-to-reach areas (e.g., back).
- Lightweight and less messy.
- Cautions:
- Ensure even coverage and avoid spraying near the face or in unventilated areas.
4. Roll-Ons
- Best For: Small, targeted areas.
- Advantages:
- Compact and precise application.
- Great for touch-ups during the day.
- Use Case: Convenient for travel or applying sunscreen to specific areas like the nose, ears, or around the eyes.
5. Sticks
- Best For: Sensitive areas or on-the-go use.
- Advantages:
- Portable and mess-free.
- Effective for areas like the lips, nose, and under the eyes.
- Use Case: Excellent for quick application and reapplication during outdoor activities.
6. Tinted Formulas
- Best For: Daily facial use with added cosmetic benefits.
- Advantages:
- Provides sun protection while evening out skin tone.
- Often less likely to leave a white cast on darker skin tones.
- Use Case: Doubles as a light makeup base.
7. Powders
- Best For: Oily skin or reapplication over makeup.
- Advantages:
- Helps control shine while providing sun protection.
- Easy to reapply without disturbing makeup.
- Use Case: Perfect for mid-day touch-ups, especially for oily or combination skin.

Key Tips
- Always choose a sunscreen labeled broad-spectrum with SPF 30 or higher.
- For outdoor or water activities, opt for water-resistant formulations.
- Match the vehicle to your skin type and the level of convenience you need.
By selecting the right vehicle, you can ensure your sunscreen fits seamlessly into your routine, making it easier to maintain consistent sun protection.
Safety
The safety of sunscreen often becomes the "elephant in the room" during discussions about skincare. Decades of research have established that sunscreen is a safe and essential tool for protecting against harmful UV radiation, which can cause skin cancer, premature aging, and other damage. Both chemical and mineral sunscreens undergo rigorous testing to ensure their efficacy and safety for human use.
While some concerns have been raised about certain chemical ingredients like oxybenzone potentially causing hormonal disruptions or harming marine life, these effects are minimal in humans at typical usage levels. Moreover, many formulations now exclude such ingredients to address these worries. Mineral sunscreens, containing zinc oxide or titanium dioxide, are generally recognized as safe and are especially recommended for sensitive skin.
The FDA has not banned any sunscreens at this stage. There have not been any reports of serious side effects from sunscreen products related to systemic absorption. In fact, the FDA has announced on its website that "given the recognized public health benefits of sunscreen use, Americans should continue to use sunscreen and other sun protective measures as this important rulemaking effort moves forward."
The bottom line is that the benefits of using sunscreen far outweigh any potential risks.

As always, it’s important to consult your dermatologist for personalized advice and recommendations tailored to your skin type and specific needs.

















